NK Cell Antibodies
Background
NK cells are an important type of innate immune lymphocytes, mainly distributed in peripheral blood and lymphoid tissues. This type of cell can recognize and kill tumor cells and virus-infected cells without pre-sensitization, playing a key role in immune surveillance. First discovered by Kiessling and Herberman in 1975, NK cells are named for their "natural killing" property. Its surface expresses a variety of activating and inhibitory receptors, precisely regulating cytotoxic functions by dynamically balancing these signals. The unique killing mechanism of NK cells (such as the release of perforin and granzyme) provides new ideas for cancer immunotherapy. Currently, NK cell-based therapies have become an important research direction in tumor biological treatment.
Structure of NK Cell
NK cells, as the core effector cells of the innate immune system, rely on the synergistic effect of multiple characteristic receptor molecules on their surface for their function: the killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) family specifically recognizes MHC class I molecules through 2-3 immunoglobulin-like domains. C-type lectin-like receptors (such as NKG2D) utilize carbohydrate recognition domains to bind stress-induced ligands; Natural cytotoxic receptors (such as NKp46) directly participate in target cell recognition through the immunoglobulin superfamily domain, and these receptors together form a precise recognition and regulatory network.
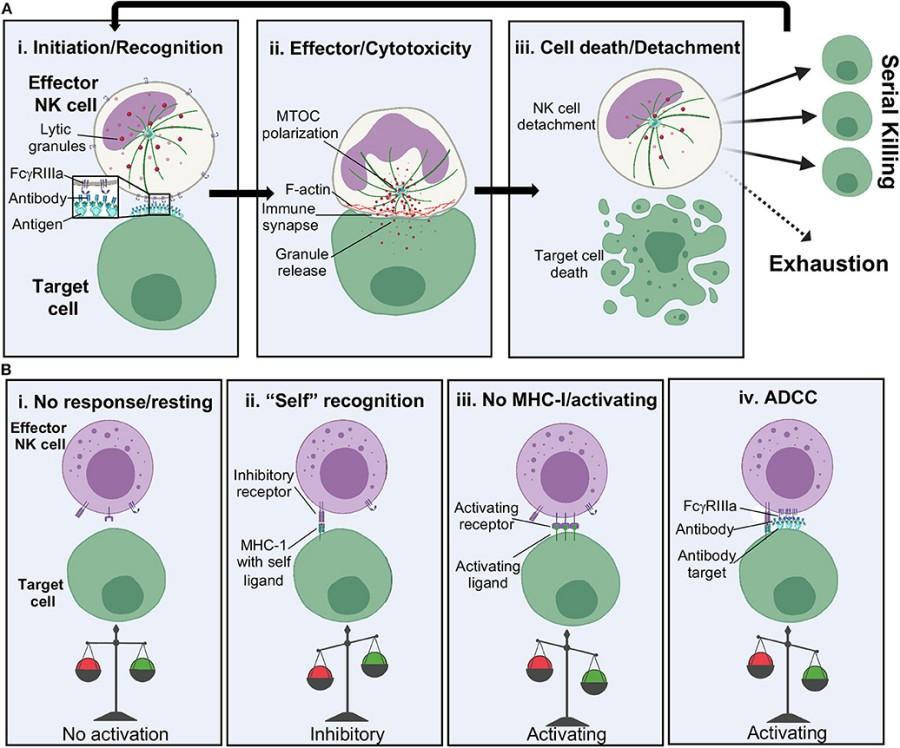 Fig. 1 NK cell cytolytic activation.1
Fig. 1 NK cell cytolytic activation.1
Key structural properties of NK cell:
- Across the membrane area and cohesion protein (DAP10/12) decoupled form complex signal transduction
- Intracellular segments contain immunoreceptor tyrosine activation motifs (ITAM) or inhibition motifs (ITIM)
- Receptors regulate cytotoxic functions through synergistic effects
- Glycosylation modification affects the binding affinity between receptors and ligands
Functions of NK Cell
The core function of NK cells is to mediate the immune surveillance and killing of abnormal cells, and they are also involved in various immune regulatory processes.
| Function | Description |
| Cytotoxic killing | Direct killing of tumor cells and virus-infected cells by the release of perforin and granzyme is the first line of defense of innate immunity. |
| Antibody-dependent cytotoxicity (ADCC) | FcγRIIIa (CD16) was used to recognize the target cells coated with antibodies and enhance the specific killing effect. |
| Immune regulation | Secrete cytokines such as IFN-γ and TNF-α to regulate the immune responses of T cells and macrophages. |
| Regulation of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) | Balance the leukemia effect of grafts and the risk of GVHD after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. |
| Maintenance of tissue homeostasis | By eliminating senescent and damaged cells, it participates in tissue repair and homeostasis regulation. |
The activation of NK cells follows a "missing self" recognition pattern. Inhibitory receptors (such as KIR) bind to MHC Class I molecules to inhibit the killing function, while activating receptors (such as NKG2D) recognize stress ligands to trigger cytotoxicity. This dual regulatory mechanism ensures the precise identification of abnormal cells.
Applications of NK Cell and NK Cell Antibody in Literature
1. Murin, Charles D. "Considerations of antibody geometric constraints on NK cell antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity." Frontiers in Immunology 11 (2020): 1635. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.01635
This article reviews the molecular mechanisms of the interaction between antibody characteristics (such as subtypes and glycosylation) and FcγRIIIa receptors in antibody-dependent cytotoxicity (ADCC) of NK cells, explores the influence of spatial geometric features of immune synapses on activation signals, and looks forward to the promoting effect of high-throughput technology on the development of NK cell therapeutic drugs.
2. Wang, Wei, et al. "NK cell-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in cancer immunotherapy." Frontiers in immunology 6 (2015): 368. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00368
This article demonstrates that myoglobin plays a central role in rhabdomyolysis- and crush syndrome-associated acute kidney injury (RM/CS-AKI), and highlights the potential of a high-affinity anti-myoglobin rabbit monoclonal antibody (RabMAb) as an effective emergency treatment that blocks myoglobin-induced kidney toxicity.
3. Seidel, Ursula JE, Patrick Schlegel, and Peter Lang. "Natural killer cell mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in tumor immunotherapy with therapeutic antibodies." Frontiers in immunology 4 (2013): 76. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2013.00076
The article indicates that over the past decade, multiple therapeutic antibodies approved by the FDA/EMA have relied on NK cell-mediated ADCC effects. The mismatch between the FcγRIIIa-V158F polymorphism and the KIR ligand affects the clinical efficacy, and antibody engineering modification is further enhancing the activity of ADCC. This article reviews the relevant mechanisms and therapeutic applications.
4. Campbell, Kerry S., Adam D. Cohen, and Tatiana Pazina. "Mechanisms of NK cell activation and clinical activity of the therapeutic SLAMF7 antibody, elotuzumab in multiple myeloma." Frontiers in immunology 9 (2018): 2551. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.02551
The article indicates that elotuzumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting SLAMF7, activates NK cells through a dual mechanism: the CD16-mediated ADCC effect and the synergistic stimulation of the SLAMF7-EAT-2 signaling pathway enhance the immunotherapy for multiple myeloma and produce a synergistic effect with drugs such as lenalidomide.
5. Khan, Muhammad, Sumbal Arooj, and Hua Wang. "NK cell-based immune checkpoint inhibition." Frontiers in immunology 11 (2020): 167. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.00167
The article indicates that NK cell immune checkpoint therapy has become a new direction in cancer treatment. Besides the classic KIRs/NKG2A, new targets such as PD-1, TIGIT, and Siglec-7/9 have emerged one after another. The dual-checkpoint blockade and combined ADCC enhancement strategy can synergistically improve the anti-tumor efficacy.
Creative Biolabs: NK Cell Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality NK cell antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for Functional assays, Flow Cytometry, Intracellular staining, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom NK Cell Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our NK Cell antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, please contact us.
Reference
- Murin, Charles D. "Considerations of antibody geometric constraints on NK cell antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity." Frontiers in Immunology 11 (2020): 1635. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.01635
Anti-NK Cell antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AFM Recombinant Antibody (V2-634159) (CBMAB-AP185LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AFDN Recombinant Antibody (V2-58751) (CBMAB-L0408-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-A2M Recombinant Antibody (V2-178822) (CBMAB-A0036-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (ALB9) (CBMAB-0176CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AP4E1 Recombinant Antibody (32) (CBMAB-A2996-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRE5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-360335) (CBMAB-C2088-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ESR1 Recombinant Antibody (Y31) (CBMAB-1208-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-NSUN6 Recombinant Antibody (D-5) (CBMAB-N3674-WJ)

-
Rat Anti-4-1BB Recombinant Antibody (V2-1558) (CBMAB-0953-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-EGR1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-100) (CBMAB-Z0289-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (DE2B4) (CBMAB-1122-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0442) (CBMAB-0445-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1/AKT2/AKT3 (Phosphorylated T308, T309, T305) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443454) (PTM-CBMAB-0030YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1B1 Antibody (V2-2449) (CBMAB-1001CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1728) (CBMAB-2077-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0435) (CBMAB-0437-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARIH1 Recombinant Antibody (C-7) (CBMAB-A3563-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (2Q1282) (CBMAB-C1624-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7697) (CBMAB-1869CQ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








