PAX2 Antibodies
Background
PAX2 gene encodes an important transcription factor, which belongs to PAX gene family and mainly regulates the formation of urinary system, central nervous system and sensory organs during embryonic development. This protein controls the expression of target genes by binding to specific DNA sequences and is particularly crucial for the normal development of the kidneys and eyes. Functional abnormalities of PAX2 are associated with a variety of congenital diseases, such as nephrooptic nerve syndrome (a genetic disorder characterized by kidney abnormalities and visual defects). Since its discovery in the 1990s, PAX2 has become an important model in developmental biology and disease mechanism research. The study of its regulatory network provides key clues for understanding organogenesis and cell differentiation, and has potential application value in the field of regenerative medicine.
Structure of PAX2
PAX2 is a transcription factor protein with a molecular weight of approximately 48 kDa. Its precise molecular weight varies slightly among different species, mainly due to the conservation of DNA-binding domains and species-specific variations in regulatory regions.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebra fish | Chicken |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 48.2 | 47.8 | 46.5 | 47.3 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains the complete pairing cassette and the octapeppeptide domain | Highly conservative, with similar functions | Partial homologous gene replication | The developmental regulation patterns are different |
The PAX2 protein is composed of approximately 400 amino acids. Its core structure consists of a highly conserved DNA-binding pairing cassette (PAX) domain and a partially conserved octapeptide domain, which jointly regulate the expression of downstream target genes. The DNA binding ability of this protein depends on the combination of β -folding and α -helix at its N-terminal, while the transcriptional activation region at the C-terminal regulates the developmental signaling pathway through protein-protein interactions. PAX2 shows a dynamic expression pattern in the development of embryonic renal ducts, optic vesicles and midbrain, and its functional deficiency can lead to abnormal organ development.
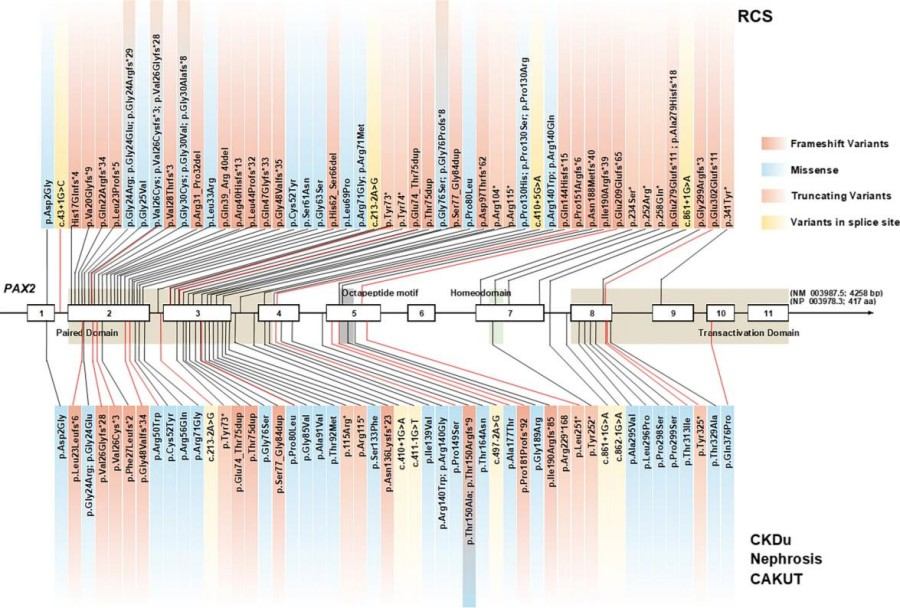 Fig. 1 Genetic variants of PAX2 that associated with kidney disease. 1
Fig. 1 Genetic variants of PAX2 that associated with kidney disease. 1
Key structural properties of PAX2:
- Conserved DNA-binding domains
- Octapeptide motif regulatory region
- Verified location signal
- Phosphorylation modification site
Functions of PAX2
The core function of the PAX2 gene is to act as a transcriptional regulatory factor in embryonic development, especially playing a key role in organ formation. At the same time, it also involves processes such as cell differentiation, maintenance of tissue homeostasis and disease occurrence.
| Function | Description |
| Regulation of kidney development | Dominant ureteral bud branching morphogenesis, regulate the nephron formation and differentiation of renal tubules. |
| Development of the visual system | Regulate the development of the optic nerve and retina, and affect the morphogenesis of the optic cup and the induction of the lens. |
| Central nervous system patterning | Participate in the midbrain - back boundary formation, affect the differentiation of neurons and neural tube closure. |
| Cell proliferation inhibition | By regulating tumor suppressor genes such as p53, tissue homeostasis is maintained and abnormal hyperplasia is prevented. |
| Tumorigenesis association | Abnormal expression is associated with the occurrence and development of tumors such as renal cell carcinoma, Wilms' tumor and glioma. |
The expression of PAX2 shows strict spatiotemporal specificity, and its dose sensitivity is manifested as follows: insufficient haploid leads to developmental defects, while overexpression may induce cancer. This gene guides the establishment of the three-dimensional configuration of target organs in a gradient-dependent manner by regulating signaling pathways such as GDNF and WNT.
Applications of PAX2 and PAX2 Antibody in Literature
1. Deng, Haiyue, et al. "Diverse phenotypes in children with PAX2-related disorder." Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine 7.6 (2019): e701. https://doi.org/10.1002/mgg3.701
This study retrospectively analyzed the clinical data of 10 children with PAX2 gene mutations and found that their phenotypes were diverse, including renal abnormalities (hypoplasia, cysts), ocular lesions and new phenotypes (skeletal deformities, ovarian teratoma, ventricular septal defect, etc.). It is reported for the first time that gout can be the initial symptom, and most of the mutations are de novo variations, suggesting that the diagnosis of this disease should be considered even without a family history. The research has expanded the phenotypic spectrum of PAX2-related diseases.
2. Muntean, Carmen, et al. "PAX2 Gene Mutation in Pediatric Renal Disorders—A Narrative Review." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.16 (2023): 12737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612737
This study found that the PAX2 gene is a key transcription factor in the development of the urinary system, and its mutation can lead to congenital malformations of the kidneys and urinary tract. This article focuses for the first time on pediatric cases of PAX2 mutations that only present with renal/urinary tract lesions, excluding patients with multiple organ involvement, providing a new perspective for revealing the pathogenic mechanism of this gene.
3. Negrisolo, Susanna, and Elisa Benetti. "PAX2 and CAKUT phenotypes: report on two New variants and a review of mutations from the Leiden Open Variation Database." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.4 (2023): 4165.https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24044165
This study found that mutations in the PAX2 gene can lead to abnormal kidney development and ocular and ear deformities (papillary kidney syndrome). This study found that 5.8% of 53 children with CAKUT carried PAX2 variations, including 2 novel mutations, confirming that their phenotypic heterogeneity was high, and even the manifestations of monozygotic twins could be different.
4. Zhang, Li, et al. "New PAX2 heterozygous mutation in a child with chronic kidney disease: a case report and review of the literature." BMC nephrology 19.1 (2018): 245.https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-018-1044-9
This study reports a 3-year-old male child with a novel missense mutation of PAX2 (Exon4 c.418C>G), presenting with chronic kidney disease and renal atrophy. His father suffered from renal failure at the age of 20, confirming that the mutation is hereditary and expanding the understanding of the pure renal phenotype of the PAX2 mutation.
5. Yamamura, Yuta, et al. "Identification of candidate PAX2-regulated genes implicated in human kidney development." Scientific reports 11.1 (2021): 9123.https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-88743-1
This study reports that the mechanism by which PAX2 gene mutations lead to renal defect syndrome (RCS) remains unclear. In this study, 189 differential promoters and 71 differential enhancers were screened out through the iPSC model, and PBX1, POSTN and ITGA9 were identified as the key target genes of PAX2 regulating renal development, providing new clues for revealing the pathogenesis of RCS.
Creative Biolabs: PAX2 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality PAX2 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom PAX2 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our PAX2 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Yang, Xue, et al. "Phenotypic spectrum and genetics of PAX2-related disorder in the Chinese cohort." BMC Medical Genomics 14.1 (2021): 250. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-021-01102-x
Anti-PAX2 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H3 (Lys36) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623395) (CBMAB-CP0994-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0059) (CBMAB-0059-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AZGP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-007) (CBMAB-Z0012-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (SN3) (CBMAB-C1037-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-EMP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0100) (CBMAB-E0207-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AP2M1 (Phosphorylated T156) Recombinant Antibody (D4F3) (PTM-CBMAB-0610LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXA3 Recombinant Antibody (2A9) (CBMAB-0377-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ASTN1 Recombinant Antibody (H-9) (CBMAB-1154-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-NSUN6 Recombinant Antibody (D-5) (CBMAB-N3674-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-CCS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1093) (CBMAB-C1150-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (H14) (CBMAB-E1341-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD164 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0077) (CBMAB-C0086-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-DMPK Recombinant Antibody (CBYCD-324) (CBMAB-D1200-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARSA Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A799) (CBMAB-A3679-YC)

-
Rat Anti-(1-5)-α-L-Arabinan Recombinant Antibody (V2-501861) (CBMAB-XB0003-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AMH Recombinant Antibody (5/6) (CBMAB-A2527-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-C4B Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C2996) (CBMAB-C4439-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (71) (CBMAB-1241CQ)

-
Rat Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (8D6) (CBMAB-C9139-LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








