PHOX2B Antibodies
Background
The PHOX2B gene is a key gene encoding homologous domain transcription factors and is mainly expressed in the development of the autonomic nervous system, especially involved in neuronal differentiation and the directed migration of neural crest cells. This gene plays a core role in physiological functions such as respiratory control, intestinal peristalsis and heart rate regulation by regulating the expression of downstream target genes. Its mutations are closely related to genetic diseases such as congenital central hypopnea syndrome (CCHS), and the clinical manifestations are abnormal autonomic nerve regulation. After its first identification in 1997, PHOX2B, due to its pivotal position in the neurodevelopmental pathway, has become an important model for studying the molecular mechanisms of autonomic nervous system diseases, greatly promoting the progress of related diagnostic strategies and targeted therapy research.
Structure of PHOX2B
PHOX2B is a transcription factor protein with a molecular weight of approximately 31 kDa. This value fluctuates to some extent among different species due to differences in the length of polyalanine repeat sequences.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebrafish |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | About 31 | About 30 | About 28 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Repetitive sequence containing 20 alanine | 15 alanine repetitive sequence | There was no polyalanine repeat expansion |
This protein is composed of 314 amino acids, and its primary structure includes a homologous domain and a helical-ring-helical domain responsible for protein dimerization. The core functional structure of PHOX2B is its C-terminal homologous domain, which directly binds to the DNA target sequence through a specific helical motif. The length of the polyalanine repeat sequence at the N-terminal of the protein is crucial for the stability and function of the protein. The abnormal expansion of this region is the main pathogenic mechanism leading to congenital central hypopnea syndrome.
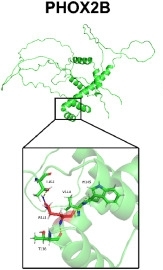 Fig. 1 3D modeling of the mutated PHOX2B protein.1
Fig. 1 3D modeling of the mutated PHOX2B protein.1
Key structural properties of PHOX2B:
- Contains homology domains for specific DNA recognition and binding
- Polymerization structure with spiral - ring - screw two domains
- N-terminal polyalanine repeats determine protein stability
- Mutations mainly occur in alanine repeat regions and homologous domains
Functions of PHOX2B
The core function of the PHOX2B gene is to regulate the development and differentiation of the autonomic nervous system. Its main physiological functions include:
| Function | Description |
| Regulation of neuronal differentiation | In autonomic ganglia, retina and brain stem decide fate of neurons in a particular area, can promote the catecholamine neuron differentiation of mature. |
| Establishment of neural circuits | Guide the formation and precise connection of key autonomic reflex arcs such as respiratory control and heart rate regulation. |
| Gene expression cascade initiation | As a transcription factor, it activates downstream target genes (such as BDNF, RET, etc.), promoting a cascade reaction in the development of the nervous system. |
| Abnormal function under pathological conditions | The mutations can lead to autonomic nerve function disorder, characterized by congenital central hypoventilation syndrome (the CCHS) and HeShenPeng disease, etc. |
PHOX2B forms a regulatory network through synergistic interaction with other transcription factors (such as ASCLL), and its activation of target genes has a high sequence specificity. This characteristic determines its irreplaceable dominant position in the development of the autonomic nervous system.
Applications of PHOX2B and PHOX2B Antibody in Literature
1. Soto-Perez, J., et al. "Phox2b-expressing neurons contribute to breathing problems in Kcnq2 loss-and gain-of-function encephalopathy models." Nature Communications 14.1 (2023): 8059. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-43834-7
This study reveals that in ventral lateral neurons expressing Phox2b, the specific expression of Kcnq2 is the key factor that makes them vulnerable to pathogenic mutations. The deletion of Kcnq2 or the gain-of-function mutation R201C respectively led to enhanced resting respiration or weakened central chemical reflex in mice, which clarified the specific mechanism of abnormal respiration in KCNQ2 encephalopathy.
2. Cardani, Silvia, et al. "Knockdown of PHOX2B in the retrotrapezoid nucleus reduces the central CO2 chemoreflex in rats." Elife 13 (2024): RP94653. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.94653
This study reveals that PHOX2B in the RTN region of the respiratory center of adult rats is the key to maintaining the chemical reflex of carbon dioxide. After specifically reducing the expression of PHOX2B in this region, although it does not affect hypoxic ventilation, it will damage the ventilation response under high carbon dioxide stimulation and reduce the expression of genes related to chemical sensitivity. This indicates that PHOX2B continuously participates in respiratory regulation in adulthood, and its insufficient expression may lead to chemical reflex defects in congenital central hypopnea syndrome (CCHS).
3. Ferreira, Caroline B., et al. "Phox2b mutation mediated by Atoh1 expression impaired respiratory rhythm and ventilatory responses to hypoxia and hypercapnia." Elife 11 (2022): e73130. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.73130
This study focuses on non-polyalanine amplification mutations (NPARM) of the PHOX2B gene. Research has found that this mutation damages the chemosensory neurons in the ventral lateral region (RTN) of mice, causing severe impairment of their ventilation response to hypoxia and hypercapnia during the neonatal period, and the hypoxia response remains partially abnormal in adulthood. This provides new evidence for revealing the pathological mechanism of this type of congenital central hypoventilation syndrome (CCHS).
4. Peggion, Sara, et al. "Revisiting Neuroblastoma: Nrf2, NF-κB and Phox2B as a Promising Network in Neuroblastoma." Current Issues in Molecular Biology 46.4 (2024): 3193-3208. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46040200
This review suggests that in neuroblastoma, the transcription factor Phox2B may form a key interaction triangular network with NF-κB and Nrf2. Phox2B drives the survival and proliferation of tumor cells by regulating genes such as RET. If the signal network composed of Phox2b and the other two factors is imbalanced, it may trigger a more aggressive tumor phenotype. This mechanism is expected to become a new therapeutic target.
5. Ke, Caiping, et al. "Novel PHOX2B germline mutation in childhood medulloblastoma: A case report." Hereditary Cancer in Clinical Practice 19.1 (2021): 12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13053-021-00170-5
In this study, an 11-year-old child with medulloblastoma was found to carry a novel germline mutation of the PHOX2B gene. This mutation was confirmed by sequencing of multiple body tissue samples, and the family history was negative, suggesting that it might be a potential cause of this childhood tumor. This discovery supports the clinical value of germline mutation screening for the families of the affected children.
Creative Biolabs: PHOX2B Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality PHOX2B antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom PHOX2B Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our PHOX2B antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Wu, Xiongwei, et al. "Identifying a novel PHOX2B gene variant in a neuroblastoma family: A case report." Heliyon 10.4 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26581
Anti-PHOX2B antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ALDOA Recombinant Antibody (A2) (CBMAB-A2316-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-dsDNA Recombinant Antibody (22) (CBMAB-AP1954LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (DE2B4) (CBMAB-1122-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0435) (CBMAB-0437-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CDK7 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C1783) (CBMAB-C3221-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT2 (Phosphorylated S474) Recombinant Antibody (V2-556130) (PTM-CBMAB-0605LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CALR Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0763) (CBMAB-C0818-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 (Phosphorylated S473) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505430) (PTM-CBMAB-0067LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM29 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179787) (CBMAB-A1149-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCL18 Recombinant Antibody (64507) (CBMAB-C7910-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CECR2 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-2465) (CBMAB-C3533WJ)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y185) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443434) (PTM-CBMAB-0001YC)

-
Rat Anti-CD63 Recombinant Antibody (7G4.2E8) (CBMAB-C8725-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC7 Recombinant Antibody (88C570) (CBMAB-L0261-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-CARTPT Recombinant Antibody (113612) (CBMAB-C2450-LY)

-
Rat Anti-AChR Recombinant Antibody (V2-12500) (CBMAB-0990-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-APOE Recombinant Antibody (A1) (CBMAB-0078CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CAPZB Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0944) (CBMAB-C2381-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (R63) (CBMAB-C9553-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BRD3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0801) (CBMAB-0804-YY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






