CNN1 Antibodies
Background
Calponin 1, encoded by the CNN1 gene, is an actin binding protein mainly expressed in smooth muscle cells of vertebrates. This protein participates in maintaining the contractile function and tension homeostasis of smooth muscle by regulating the interaction between actin and myosin and inhibiting the activity of myosin ATPase. During vascular development, CNN1 regulates vascular morphogenesis through cytoskeletal recombination, and its abnormal expression is closely related to vascular lesions such as atherosclerosis and hypertension. This gene was first identified in 1991. The protein it encodes has become a marker of smooth muscle cell differentiation and holds significant model value for studying cytoskeletal dynamics, mechanical signal transduction, and the mechanisms of vascular diseases.
Structure of CNN1
The molecular weight of Calponin 1 encoded by the CNN1 gene is approximately 34 kDa, and this value fluctuates slightly among different species due to differences in amino acid sequences.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 34 | 33.5 | 33.8 | 34.2 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contain 3 CH structural domain | The second CH domain has two amino acid substitutions | Highly similar to the human sequence | There is a minor variation in the C-terminal sequence |
This protein is composed of 292 amino acids, and its primary structure forms three typical calcium-regulated protein homologous (CH) domains. The protein core binds to actin filaments through these domains, among which the first CH domain inhibits myosin ATPase activity. The conserved "KKLR" motif mediates the interaction with the cytoskeleton, while the N-terminal region plays a key role in regulating smooth muscle contraction.
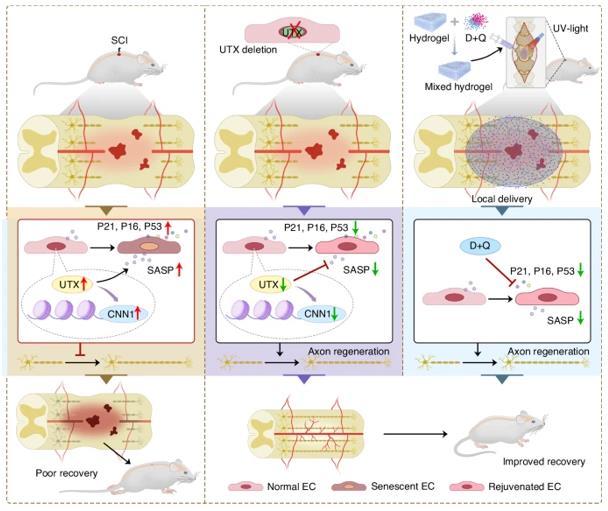 Fig. 1 A schematic of UTX/CNN1 axis in the regulation of SCMECs senescence.1
Fig. 1 A schematic of UTX/CNN1 axis in the regulation of SCMECs senescence.1
Key structural properties of CNN1:
- Contains three conserved calopsonin homeodomains
- The N-terminal region forms the actin binding core
- Conserved KKLR motifs mediate cytoskeletal interactions
Functions of CNN1
The main function of calcium-regulated protein 1 encoded by the CNN1 gene is to regulate smooth muscle contraction. Its specific physiological functions are as follows:
| Function | Description |
| Contraction regulation | By inhibiting the activity of myosin ATPase, it directly regulates the contraction strength and speed of smooth muscle. |
| Cytoskeleton stability | As a structural adaptor protein, it maintains the mechanical integrity of the actin cytoskeleton. |
| Vascular development | In the process of embryonic angiogenesis mediated vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation and morphogenesis. |
| Mechanical conduction | Transmit mechanical signals from the extracellular matrix to the intracellular signal network of smooth muscle cells. |
| Disease association | Abnormal expression levels are closely related to vascular lesions such as atherosclerosis and hypertension. |
Calcium-regulated protein 1 binds to actin through its three CH domains and exerts regulatory effects in a calcium ion-independent manner. This characteristic distinguishes it from other contractile regulatory proteins and makes it a key target for the study of smooth muscle function.
Applications of CNN1 and CNN1 Antibody in Literature
1. Zhang, Zheng, et al. "CNN1 represses bladder cancer progression and metabolic reprogramming by modulating HIF-1α signaling pathway." Frontiers in Oncology 12 (2022): 859707. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.859707
This study confirmed that the low expression of CNN1 in bladder cancer is associated with a poor prognosis. Overexpression of CNN1 can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, migration and glycolytic processes of cancer cells. The mechanism may be related to the regulation of the HIF-1α pathway, suggesting that CNN1 is expected to become a new target for the diagnosis of bladder cancer.
2. Li, Chengjun, et al. "Kdm6a-CNN1 axis orchestrates epigenetic control of trauma-induced spinal cord microvascular endothelial cell senescence to balance neuroinflammation for improved neurological repair." Bone Research 12.1 (2024): 19. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41413-024-00323-x
Research has revealed that the combination of UTX and CNN1 forms an epigenetic regulatory axis, inducing senescence of spinal microvascular endothelial cells and the release of inflammatory factors, and promoting neuroinflammation. Targeting this axis may provide a new strategy for spinal cord injury repair.
3. de Sousa Portilho, Adrhyann Jullyanne, et al. "1, 4-Naphthoquinone (CNN1) induces apoptosis through DNA damage and promotes upregulation of H2AFX in Leukemia multidrug resistant cell line." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23.15 (2022): 8105. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158105
This study explored the effect of compound CNN1 on drug-resistant leukemia cells. The results show that CNN1 can effectively induce apoptosis of drug-resistant cells by disrupting the functions of cell membranes and mitochondria, causing DNA damage and cell cycle arrest, demonstrating potential in the treatment of drug-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia.
4. Mele, Valentina, et al. "Identification of TPM2 and CNN1 as novel prognostic markers in functionally characterized human colon cancer-associated stromal cells." Cancers 14.8 (2022): 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14082024
Research has found that CNN1 and TPM2, which are highly expressed in colon cancer stromal cells, are novel markers that can significantly promote tumor metastasis and are closely related to the poor prognosis of patients. Their predictive value is superior to existing indicators.
5. Yi, Dandan, et al. "Long non-coding RNA MEG3 acts as a suppressor in breast cancer by regulating miR-330/CNN1." Aging (Albany NY) 16.2 (2024): 1318. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205419
Studies have shown that the long non-coding RNA MEG3 inhibits the progression of breast cancer by adsorbing miR-330 and upregulating the expression of the tumor suppressor gene CNN1. High expression of CNN1 is associated with a good prognosis for patients.
Creative Biolabs: CNN1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality CNN1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom CNN1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our CNN1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Li, Chengjun, et al. "Kdm6a-CNN1 axis orchestrates epigenetic control of trauma-induced spinal cord microvascular endothelial cell senescence to balance neuroinflammation for improved neurological repair." Bone Research 12.1 (2024): 19. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41413-024-00323-x
Anti-CNN1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CAT Recombinant Antibody (724810) (CBMAB-C8431-LY)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR-0120) (CBMAB-R0120-FY)

-
Rat Anti-AChR Recombinant Antibody (V2-12500) (CBMAB-0990-CN)

-
Rat Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (8D6) (CBMAB-C9139-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0138) (CBMAB-0139-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ABIN2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179106) (CBMAB-A0349-YC)

-
Rat Anti-CD34 Recombinant Antibody (MEC 14.7) (CBMAB-C10196-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD1C Recombinant Antibody (L161) (CBMAB-C2173-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-CBL Recombinant Antibody (D4E10) (CBMAB-CP0149-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AFM Recombinant Antibody (V2-634159) (CBMAB-AP185LY)

-
Mouse Anti-EMP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0100) (CBMAB-E0207-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (CBLNB-121) (CBMAB-1180-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-C4B Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C2996) (CBMAB-C4439-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV8 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634028) (CBMAB-AP022LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CARD11 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0811) (CBMAB-C0866-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-DISP2 Monoclonal Antibody (F66A4B1) (CBMAB-1112CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD83 Recombinant Antibody (HB15) (CBMAB-C1765-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CCNH Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1054) (CBMAB-C1111-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD2AP Recombinant Antibody (BR083) (CBMAB-BR083LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ANXA7 Recombinant Antibody (A-1) (CBMAB-A2941-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








