EN1 Antibodies
Background
The EN1 gene, as an important homologous box transcription factor, is mainly expressed during embryonic development and is particularly involved in the pattern construction of the central nervous system, limb formation and craniofacial structure. This gene dominates the spatial localization and cell differentiation process of multiple organ development by regulating the transcriptional activity of downstream target genes. In vertebrates, abnormal expression of EN1 can lead to congenital defects such as neural tube closure disorders and limb deformities, and its functional deficiency is closely related to diseases such as spina bifida in humans. Since its discovery in the early 1990s, EN1 has become a key molecule in developmental biology research. The study of its regulatory network not only reveals the molecular mechanism of embryonic morphogenesis but also provides important pathological explanations for congenital diseases. The high conservation of this gene during the evolutionary process further highlights its fundamental role in the animal developmental system.
Structure of EN1
The molecular weight of the transcription factor encoded by the EN1 gene is approximately 41.8 kDa, and its specific value varies slightly among different species.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebrafish | Chicken |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 41.8 | 41.7 | 40.9 | 41.5 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Containing 331 amino acids, conserved homologous domain | Serine at the 12th position is substituted | The homologous domain sequences are 85% similar | Highly conserved DNA binding area |
This protein is composed of 331 amino acids, and its primary structure contains a typical 60-amino acid homologous domain. The secondary structure of the EN1 protein is mainly composed of an α-helix, in which the amino acids at positions 25 to 35 form a helical - turning - helical DNA-binding motif. The DNA binding specificity of this protein is determined by arginine at position 50 and tryptophan at position 53, and these conserved residues form a hydrogen bond network with the target DNA groove. During the evolution of vertebrates, the homologous domain sequence of the EN1 protein remains highly conserved, while the non-domain regions show a relatively high species-specific variation.
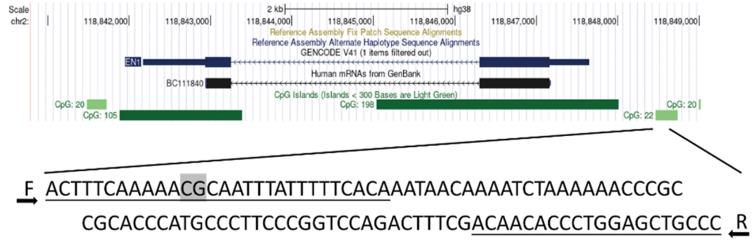 Fig. 1 Target sequences in the EN1 promoter region.1
Fig. 1 Target sequences in the EN1 promoter region.1
Key structural properties of EN1:
- Conserved homologous domains form helix-turn-helical structures
- DNA binding domain has the hydrophobic core
- Specific ring structure determines DNA sequence recognition specificity
Functions of EN1
The core function of the EN1 gene is to regulate morphogenesis and cell differentiation during embryonic development, and it also participates in the maintenance and repair of the nervous system in adulthood.
| Function | Description |
| Neural tube pattern formation | Guide the specialization of the midbrain - posterior brain boundary in the embryo to ensure the correct establishment of the anterior and posterior axes of the central nervous system. |
| Regulation of limb development | Regulate the FGF signaling pathway of the spinous apical ectodermal ridge of the limb to guide the formation of the proximal and distal axis patterns of the limb. |
| Craniofacial morphogenesis | Participate in maxillofacial of cell proliferation and differentiation of primordium, affect the growth of palate and mandible. |
| Survival and maintenance of neurons | Sustained expression in substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons prevents neuronal degeneration in adulthood. |
| Formation of skin appendages | Regulate the development of hair follicles and glands and affect the directional differentiation of keratinocytes in the skin. |
The expression of the EN1 gene shows strict spatiotemporal specificity, and its expression level is dose-dependent on the concentration of morphogenetic hormones. This is different from the synergistic effect of hemoglobin, reflecting its characteristic as a key morphological determinant during development.
Applications of EN1 and EN1 Antibody in Literature
1. Alves dos Santos, Maria TM, and Marten P. Smidt. "En1 and Wnt signaling in midbrain dopaminergic neuronal development." Neural development 6.1 (2011): 23. https://doi.org/10.1186/1749-8104-6-23
This study reveals that the development and maintenance of midbrain dopamine neurons (mdDA) depend on the synergistic effect of En1 transcription factors and the Wnt signaling pathway, which jointly regulate neuronal phenotypes, providing a key theoretical basis for cell replacement therapy for neurological diseases such as Parkinson's disease.
2. Chang, Jinchun, et al. "EN1 regulates cell growth and proliferation in human glioma cells via Hedgehog signaling." International journal of molecular sciences 23.3 (2022): 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031123
This study reveals that EN1 is highly expressed in glioblastoma and predicts a poor prognosis. It promotes tumor proliferation, migration and radiotherapy resistance by regulating the Hedgehog signaling pathway, and can serve as a potential diagnostic marker and therapeutic target.
3. Cui, Yajuan, et al. "EN1 promotes lung metastasis of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma by regulating the PI3K-AKT pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition." Cancer Cell International 24.1 (2024): 51. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-024-03230-7
This study reveals that EN1 is overexpressed in salivary gland adenoid cystic carcinoma due to promoter hypomethylation and promotes tumor metastasis by activating the PI3K-AKT pathway and EMT, which can serve as a potential diagnostic marker and therapeutic target.
4. Xu, Jihao, et al. "Engrailed‐1 Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis." Advanced Science 11.6 (2024): 2308537. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202308537
This study reveals that EN1 is abnormally expressed in pancreatic cancer with a poor prognosis. It promotes tumor transformation and metastasis by regulating the MAPK pathway and inducing interstitial surface, and is a potential new therapeutic target.
5. Trevisan, Alexandra J., et al. "The transcriptomic landscape of spinal V1 interneurons reveals a role for En1 in specific elements of motor output." BioRxiv (2024). https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.09.18.613279
This study reveals that the transcription factor En1 specifically determines the V1Pou6f2 interneuron subpopulation in the spinal cord. Its absence selectively disrupts the frequency of rhythmic motor output, but does not affect limb flexion and extension movements.
Creative Biolabs: EN1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality EN1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom EN1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our EN1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Cui, Yajuan, et al. "EN1 promotes lung metastasis of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma by regulating the PI3K-AKT pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition." Cancer Cell International 24.1 (2024): 51. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-024-03230-7
Anti-EN1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rabbit Anti-DLK1 Recombinant Antibody (9D8) (CBMAB-D1061-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0845) (CBMAB-F0462-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7697) (CBMAB-1869CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD1C Recombinant Antibody (L161) (CBMAB-C2173-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BANF1 Recombinant Antibody (3F10-4G12) (CBMAB-A0707-LY)

-
Rat Anti-FABP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-2299) (CBMAB-F1612-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ACLY Recombinant Antibody (V2-179314) (CBMAB-A0610-YC)

-
Rat Anti-CCR2 Recombinant Antibody (475301) (CBMAB-C1338-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AHCYL1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180270) (CBMAB-A1703-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (E-2) (CBMAB-A3358-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AGK Recombinant Antibody (V2-258056) (CBMAB-M0989-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CAMK2A Recombinant Antibody (BA0032) (CBMAB-0137CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ATG5 Recombinant Antibody (9H197) (CBMAB-A3945-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-363290) (CBMAB-S0173-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B1 Recombinant Antibody (E4) (CBMAB-0463-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (H14) (CBMAB-E1341-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1/AKT2/AKT3 (Phosphorylated T308, T309, T305) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443454) (PTM-CBMAB-0030YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DLG1 Monolconal Antibody (4F3) (CBMAB-0225-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-EIF4G1 Recombinant Antibody (2A9) (CBMAB-A2544-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTN4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-6075) (CBMAB-0020CQ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






