LYAR Antibodies
Background
The LYAR gene encodes a zinc finger protein located in the nucleolus and is mainly expressed in tissues with active cell proliferation. This protein participates in embryonic development and the maintenance of tissue homeostasis by regulating ribosome biosynthesis and cell cycle processes. Studies have found that LYAR is abnormally highly expressed in various tumors and drives tumorigenesis by inhibiting apoptosis and promoting G1/S phase transition. Its molecular mechanism involves interaction with RNA-binding proteins, thereby influencing the post-transcriptional regulation of target genes. Due to its crucial role in cell proliferation, LYAR has become a potential molecular target of great concern in the field of cancer treatment, and related research has provided important clues for revealing the mechanism of malignant cell transformation.
Structure of LYAR
LYAR is a zinc finger protein with a molecular weight of approximately 55-60 kDa. Its precise molecular weight may vary among different transcripts and post-translational modifications.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebrafish |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 58.5 | 57.8 | 55.2 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains nucleolar localization signals and three zinc finger domains | Highly homologous to humans and functionally conserved | Structure domain composition similar, but low homology |
This protein is composed of approximately 500 amino acids, and its core function relies on typical C2H2-type zinc finger domains, which mediate interactions with nucleic acids and proteins. The tertiary structure of LYAR forms a compact spherical conformation, with its zinc finger modules arranged like "fingers", which can precisely recognize and bind to specific DNA or RNA sequences, thus playing a key role in ribosome biosynthesis and cell cycle regulation.
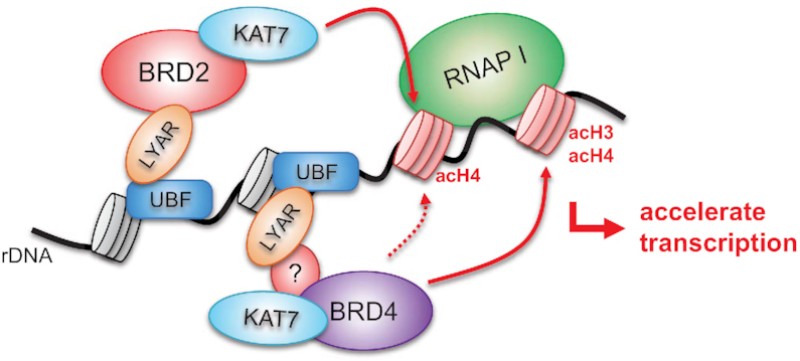 Fig. 1 LYAR-Mediated Recruitment of BRD2-KAT7 Drives H4 Acetylation and rDNA Transcription.1
Fig. 1 LYAR-Mediated Recruitment of BRD2-KAT7 Drives H4 Acetylation and rDNA Transcription.1
Key structural properties of LYAR:
- Typical C2H2 zinc finger domain is the core module
- Nucleolus localization signals ensure their functional localization within the cell nucleus
- Zinc ion coordination system maintains structural stability and nucleic acid binding ability
Functions of LYAR
The main function of the LYAR gene is to regulate cell proliferation and survival. However, it is also involved in a variety of cell biological processes, including ribosomal biogenesis and cell fate determination.
| Function | Description |
| Cell cycle regulation | Promote the transition of cells from the G1 phase to the S phase and directly drive cell proliferation, especially in stem cells and progenitor cells. |
| Ribosome biosynthesis | Within the nucleolus in ribosomal RNA processing and mature, provide basic support for protein synthesis. |
| Apoptosis inhibition | By regulating the expression of related genes, it inhibits programmed cell death and supports cell survival. |
| Embryonic development participation | The high expression in early embryo, is very important to the formation of the normal tissues and organs. |
| Tumorigenesis driver | The abnormally high expression driven by the above mechanism of various types of cancer, such as liver cancer, leukemia, malignant progression. |
LYAR plays a key role in integrating cell growth signals and proliferation execution by coordinating transcriptional regulation and nucleolar function. Its functional network is complex and at the core.
Applications of LYAR and LYAR Antibody in Literature
1. Wu, Yupeng, et al. "LYAR promotes colorectal cancer progression by upregulating FSCN1 expression and fatty acid metabolism." Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2021.1 (2021): 9979707. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9979707
Research has found that LYAR is highly expressed in colorectal cancer and promotes metastasis. The mechanism is to up-regulate FSCN1, thereby affecting fatty acid metabolism and ultimately enhancing the migration and invasion abilities of cancer cells.
2. Izumikawa, Keiichi, et al. "LYAR potentiates rRNA synthesis by recruiting BRD2/4 and the MYST-type acetyltransferase KAT7 to rDNA." Nucleic Acids Research 47.19 (2019): 10357-10372. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz747
This study found that LYAR activates rRNA transcription and promotes tumorigenesis by separately recruiting the BRD2-KAT7 and BRD4-KAT7 complexes to the rDNA region, synergically increasing the acetylation level of histone H3/H4.
3. Wu, Yupeng, et al. "LYAR promotes colorectal cancer cell mobility by activating galectin-1 expression." Oncotarget 6.32 (2015): 32890. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.5335
Studies have shown that highly expressed LYAR enhances the mobility and invasion ability of colorectal cancer cells by directly transcriptional activating LGALS1 (galectin-1), revealing a new carcinogenic mechanism.
4. Yang, Cha, et al. "The nucleolar protein LYAR facilitates ribonucleoprotein assembly of influenza A virus." Journal of Virology 92.23 (2018): 10-1128. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01042-18
This study found that the host protein LYAR interacts with the vRNP complex of influenza A virus, enhancing viral RNA synthesis by promoting the assembly of vRNP, thereby facilitating important viral replication.
5. Zuccato, Cristina, et al. "The rs368698783 (G> A) Polymorphism Affecting LYAR Binding to the Aγ-Globin Gene Is Associated with High Fetal Hemoglobin (HbF) in β-Thalassemia Erythroid Precursor Cells Treated with HbF Inducers." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.1 (2023): 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010776
This study found that the rs368698783 polymorphism of the LYAR gene reduced its binding efficiency with the promoter of the Aγ -globin gene, thereby upregulating the basal and induced levels of fetal hemoglobin (HbF), providing a basis for the precise treatment of β -thalassemia.
Creative Biolabs: LYAR Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality LYAR antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom LYAR Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our LYAR antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Izumikawa, Keiichi, et al. "LYAR potentiates rRNA synthesis by recruiting BRD2/4 and the MYST-type acetyltransferase KAT7 to rDNA." Nucleic Acids Research 47.19 (2019): 10357-10372. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz747
Anti-LYAR antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180546) (CBMAB-A2070-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD8 Recombinant Antibody (C1083) (CBMAB-C1083-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-55272) (CBMAB-H0819-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ABCA3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-178911) (CBMAB-A0145-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1093) (CBMAB-C1150-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALOX5AP Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-1219) (CBMAB-F0750-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-C5B-9 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYA-0216) (CBMAB-X0304-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1A2 Recombinant Antibody (M7-PB-E9) (CBMAB-A4013-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-363290) (CBMAB-S0173-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AMACR Recombinant Antibody (CB34A) (CBMAB-CA034LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BLK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0618) (CBMAB-0621-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-EGR1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-100) (CBMAB-Z0289-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-BRD3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0801) (CBMAB-0804-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AGK Recombinant Antibody (V2-258056) (CBMAB-M0989-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ABL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179121) (CBMAB-A0364-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARIH1 Recombinant Antibody (C-7) (CBMAB-A3563-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179329) (CBMAB-A0627-YC)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR-0120) (CBMAB-R0120-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALPL Antibody (B4-78) (CBMAB-1009CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CTNND1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2414) (CBMAB-C2487-FY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








