HKDC1 Antibodies
Background
The HKDC1 gene is a multifunctional protein widely expressed in various tissues, and its encoded products are mainly located in mitochondria and cytoplasm. This protein plays a key role in maintaining genomic stability, promoting mitochondrial function and participating in the process of DNA damage repair, and has an important impact on cell cycle regulation and energy metabolism balance. Recent studies have found that HKDC1 interacts with the outer mitochondrial membrane through a special domain at its C-terminal. This unique localization mechanism enables it to play a core role in coordinating cellular metabolism and stress responses. As a new member of the hexokinase family, its abnormal expression is closely related to various diseases such as gestational diabetes and tumorigenesis. Currently, it has become an important target in the fields of metabolic diseases and cancer research, providing a new molecular perspective for understanding the cellular metabolic regulatory network.
Structure of HKDC1
HKDC1 is a large multifunctional protein with a molecular weight of approximately 110 kDa. Its exact molecular weight may vary to some extent due to different biological species and transcript variations.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | About 110 | About 109 | About 110 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains N the sequence mitochondrial targeting and C the special structure of the domain | Highly homologous to humans, the core catalytic domain is conserved | Have similar binary positioning signals |
The HKDC1 protein contains approximately 900 amino acid residues, forming a typical hexokinase globular structure. Its primary structure contains two unique mitochondrial-targeting mods at the N-terminal and C-terminal. This dual localization signal is one of its most notable features, enabling it to be respectively located on the outer mitochondrial membrane and the cytoplasm. The secondary structure of proteins is mainly composed of α -helicles and β -folds, which together form the conserved glucose binding pocket and catalytic core. The special helical structure at its C-terminal is crucial for anchoring on mitochondria and interacting with the mitochondrial protein VDAC1, a structural feature that distinguishes it from other classical hexokinases.
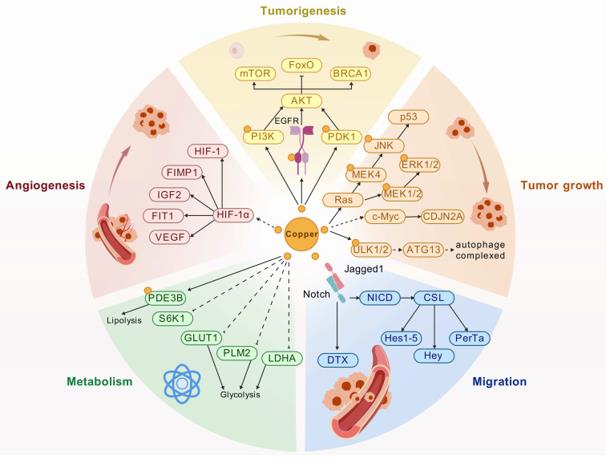 Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of regulatory mechanism of HKDC1 in cancers.1
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of regulatory mechanism of HKDC1 in cancers.1
Key structural properties of HKDC1:
- Typical double-domain hexokinase folding
- The N-terminal and C-terminal each have a mitochondrial-targeting motif
- The C-terminal contains a specific mitochondrial anchoring helical segment
Functions of HKDC1
The core function of the HKDC1 gene is to coordinate glucose metabolism with the maintenance of organelle homeostasis. Its specific physiological functions are as follows:
| Function | Description |
| Glucose phosphorylation | Catalyzing the generation of glucose-6-phosphate from glucose is the initial step and key regulatory point of the glycolytic pathway. |
| Maintenance of mitochondrial function | Anchored to the outer mitochondrial membrane through its C-terminal domain, it directly participates in maintaining the mitochondrial membrane potential and integrity. |
| Genomic stability protection | In response to DNA damage in the nucleus, it participates in the repair process of DNA double-strand breaks and prevents abnormal genetic information. |
| Regulation of autophagy process | Under cellular stress conditions, autophagic activity is affected by the interaction with mitochondria through the regulation of glucose-6-phosphate flux. |
| Metabolic reprogramming coordination | Coordinate the adaptive transition between glycolysis and mitochondrial metabolism in rapidly proliferating environments such as tumor cells. |
HKDC1, through its unique subcellular bilocalization characteristics, establishes a direct metabolic bridge between the cytoplasm and mitochondria. This spatial regulation mechanism enables it to efficiently respond to changes in energy state and maintain metabolic homeostasis, especially playing a core role in responding to metabolic stress.
Applications of HKDC1 and HKDC1 Antibody in Literature
1. Zhang, Yi, et al. "HKDC1 promotes tumor immune evasion in hepatocellular carcinoma by coupling cytoskeleton to STAT1 activation and PD-L1 expression." Nature communications 15.1 (2024): 1314. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-45712-2
The article indicates that HKDC1 promotes IFNγ -induced STAT1 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation by binding to ACTA2, upregulates tumor PD-L1 expression, and mediates immune escape. Inhibiting HKDC1 can enhance the therapeutic effect of PD-1/PD-L1 blocking, providing a new strategy for combined immunotherapy of liver cancer.
2. Luo, Xia, et al. "HKDC1 in Cancer: Mechanisms, Clinical Applications, and Future." Journal of Cancer 16.13 (2025): 3851. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.116277
The article indicates that HKDC1 is a protein highly expressed in various cancers, promoting tumor progression through mechanisms such as enhanced glycolysis and being associated with poor prognosis. Research shows that it plays a key role in tumor metabolic reprogramming and immune escape, and is expected to become a new cancer biomarker and therapeutic target.
3. Yu, Chen, et al. "HKDC1 silencing inhibits proliferation and glycolysis of gastric cancer cells." Journal of Oncology 2023.1 (2023): 3876342. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/3876342
The article indicates that HKDC1 functions as an oncogene in gastric cancer. Studies have shown that knocking down HKDC1 can inhibit the proliferation ability of gastric cancer cells and weaken their glycolytic process by reducing glucose uptake, lactic acid production and ATP levels, while enhancing the oxygen consumption rate. This confirms that HKDC1 promotes the development of gastric cancer by regulating cell proliferation and glycolysis.
4. Khan, Md Wasim, et al. "The hexokinase "HKDC1" interaction with the mitochondria is essential for liver cancer progression." Cell death & disease 13.7 (2022): 660. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-04999-z
The article indicates that HKDC1 is highly expressed in liver cancer and is a key mitochondrial protein. Studies have shown that knocking out HKDC1 can cause mitochondrial dysfunction, leading to insufficient cellular energy supply and inhibiting tumor growth through metabolic reprogramming. Given its low expression in normal liver cells, targeting HKDC1 and its mitochondrial interaction provides a highly selective new strategy for the treatment of liver cancer.
5. Huang, Shansong, et al. "HKDC1 promotes colorectal cancer progression by regulating RCOR1 expression to activate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, enhancing proliferation, migration, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition." Journal of Biological Chemistry 301.5 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108478
The article indicates that HKDC1 is highly expressed in colorectal cancer and is associated with a poor prognosis. The study for the first time revealed that HKDC1 activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by binding to RCOR1, thereby promoting the proliferation, migration, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and glycolysis of tumor cells. This indicates that HKDC1 is a potential prognostic marker and a new therapeutic target for colorectal cancer.
Creative Biolabs: HKDC1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality HKDC1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom HKDC1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our HKDC1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Luo, Xia, et al. "HKDC1 in Cancer: Mechanisms, Clinical Applications, and Future." Journal of Cancer 16.13 (2025): 3851. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.116277
Anti-HKDC1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rat Anti-AChR Recombinant Antibody (V2-12500) (CBMAB-0990-CN)

-
Rat Anti-EPO Recombinant Antibody (16) (CBMAB-E1578-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-DES Monoclonal Antibody (440) (CBMAB-AP1857LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCNH Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1054) (CBMAB-C1111-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503417) (CBMAB-V208-1369-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-COL12A1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C3117) (CBMAB-C4560-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BSN Recombinant Antibody (219E1) (CBMAB-1228-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (H14) (CBMAB-E1341-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP5F1A Recombinant Antibody (51) (CBMAB-A4043-YC)

-
Rat Anti-EMCN Recombinant Antibody (28) (CBMAB-E0280-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD59 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2097) (CBMAB-C4421-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AMH Recombinant Antibody (5/6) (CBMAB-A2527-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALPL Antibody (B4-78) (CBMAB-1009CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BRD3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0801) (CBMAB-0804-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0435) (CBMAB-0437-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CAP219) (CBMAB-AP536LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCDC6 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0106) (CBMAB-C5397-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y185) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443434) (PTM-CBMAB-0001YC)

-
Rat Anti-ADGRE4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-160163) (CBMAB-F0011-CQ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






