SOX3 Antibodies
Background
The SOX3 gene belongs to the SOX (SRY-related HMG-box) transcription factor family and is mainly expressed during the development of the central nervous system. This gene specifically binds to DNA through the HMG domain it encodes and participates in regulating key biological processes such as the maintenance, differentiation of neural stem cells and the development of the pituitary gland. Research has found that mutations in the SOX3 gene are closely related to genetic diseases such as X-linked intellectual disability and hypopituitarism. As one of the early identified SRY-related genes, SOX3 has become an important model in developmental biology research due to its dual regulatory role in sex determination and neurodevelopment, providing a key theoretical basis for understanding the functional mechanisms of transcription factors in embryonic development.
Structure of SOX3
The molecular weight of the protein encoded by the SOX3 gene is approximately 32.8 kDa, and its exact value varies slightly among different species due to differences in amino acid sequences.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebrafish | African clawed toad |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 32.8 | 33.1 | 32.5 | 32.9 |
| Primary Structural Differences | The typical structure of HMG domain | Very high homology with humans | Highly conservative in the HMG-box area | Specific sequence variation exists at the carboxyl terminus |
This protein contains approximately 300 amino acids, and its functional core is a HMG-box domain composed of about 79 amino acids. This domain regulates gene transcription by inducing DNA bending. The nuclear localization signal of proteins ensures their localization within the cell nucleus. The SOX3 protein adopts a unique structural model. Its HMG domain is composed of three α -helices, which bind to DNA small grooves in a non-sequence-specific manner and force DNA to undergo significant bending. This is the structural basis for its transcriptional regulatory function.
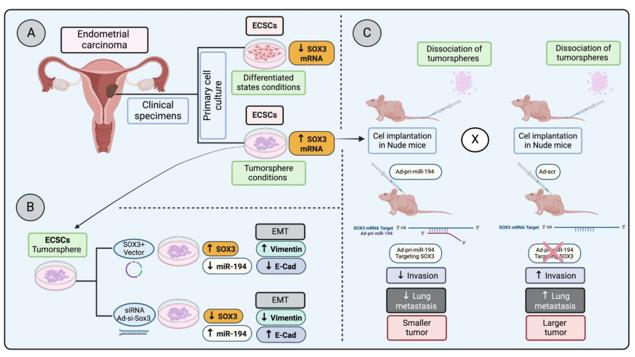 Fig. 1 Regulation of SOX3 in endometrial carcinoma progression and metastasis.1
Fig. 1 Regulation of SOX3 in endometrial carcinoma progression and metastasis.1
Key structural properties of SOX3:
- Contains the highly conserved HMG-box domain
- Utilize nuclear localization proteins with a molecular weight of approximately 25kDa
- The HMG domain forms an L-shaped 3D conformation to induce DNA bending
- Regulate the transcription of target genes through changes in DNA conformation
Functions of SOX3
The core function of the SOX3 gene is to act as a transcriptional regulatory factor in the development of the nervous system and the determination of cell fate. In addition, this gene also plays a key role in physiological processes such as sex differentiation and pituitary gland formation.
| Function | Description |
| Neurodevelopmental regulation | In embryonic neural tube high expression, through regulating target genes of proliferation and differentiation of neural precursor cells. |
| Cell fate determination | By activating or inhibiting downstream genes (such as those encoding other transcription factors), cells are guided to develop towards specific lineages. |
| Gender maintenance | Play a role in the sex determination pathway, and its dysfunction can lead to congenital diseases related to sex development. |
| Pituitary gland formation | Is essential to the anterior lobe of the normal development, the absence or mutation causes pituitary function impairment. |
| Biomarker | Due to its specific expression in various tumors, it can be studied as a diagnostic marker for cancers such as glioma. |
Unlike most widely acting transcription factors, the function of SOX3 has a high degree of spatiotemporal specificity, and its regulatory effect strongly depends on the developmental stage, cell type, and the specific regulatory network formed with other co-factors.
Applications of SOX3 and SOX3 Antibody in Literature
1. Wei, Jiansheng, et al. "Duplication of SOX3 in an SRY-negative 46, XX male with prostatic utricle: case report and literature review." BMC Medical Genomics 15.1 (2022): 188. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-022-01347-0
The article indicates that a 5-year-old male patient with negative SRY, 46, XX, carried a duplication of the SOX3 gene on the X chromosome, which led to sexual inversion and testicular dysplasia, as well as concurrent prostatic cysts and hypospadias. It is recommended that such patients undergo SOX3 mutation screening and endoscopic examination to improve the surgical prognosis.
2. Del Puerto, Helen Lima, et al. "Clinical correlation of transcription factor SOX3 in cancer: unveiling its role in tumorigenesis." Genes 15.6 (2024): 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060777
The article indicates that the SOX3 transcription factor is abnormally expressed in various cancers and affects tumor development by regulating processes such as apoptosis and invasion. Its expression level is related to the clinicopathological characteristics of patients, and its function is complex. It is a potential therapeutic research target.
3. McAninch, Dale, et al. "SOX3 promotes generation of committed spermatogonia in postnatal mouse testes." Scientific reports 10.1 (2020): 6751. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-63290-3
The article indicates that SOX3 is expressed in nerves and spermatogonia. Studies have shown that SOX3 drives the transformation of progenitor cells from self-renewal to proliferation and differentiation by directly binding to and activating the Ngn3 promoter, and it is a key factor in determining cell fate.
4. Zhou, Tong, et al. "Role of Sox3 in Estradiol-Induced sex reversal in Pelodiscus sinensis." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.1 (2023): 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010248
Research has found that the Sox3 gene of Chinese soft-shelled turtles is highly expressed in the ovaries. During estrogen-induced sexual reversal, Sox3 plays a key role in promoting ovarian differentiation by regulating signaling pathways such as Wnt and TGF-β.
5. Hong, Qiang, et al. "Loss-of-function of sox3 causes follicle development retardation and reduces fecundity in zebrafish." Protein & cell 10.5 (2019): 347-364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-018-0603-y
Studies on zebrafish have shown that the Sox3 gene inhibits follicular cell apoptosis by directly regulating the expression of cyp19a1a and promoting estrogen synthesis. This mechanism is crucial for maintaining normal follicular development and female fertility.
Creative Biolabs: SOX3 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality SOX3 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom SOX3 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our SOX3 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Del Puerto, Helen Lima, et al. "Clinical correlation of transcription factor SOX3 in cancer: unveiling its role in tumorigenesis." Genes 15.6 (2024): 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060777
Anti-SOX3 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ARIH1 Recombinant Antibody (C-7) (CBMAB-A3563-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-EMP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0100) (CBMAB-E0207-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1093) (CBMAB-C1150-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-dsDNA Recombinant Antibody (22) (CBMAB-AP1954LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APOE Recombinant Antibody (A1) (CBMAB-0078CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 (Phospho-Ser3) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1770) (CBMAB-C1832-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0435) (CBMAB-0437-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-14-3-3 Pan Recombinant Antibody (V2-9272) (CBMAB-1181-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AGK Recombinant Antibody (V2-258056) (CBMAB-M0989-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CASQ1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0863) (CBMAB-C0918-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ASH1L Monoclonal Antibody (ASH5H03) (CBMAB-1372-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1C3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12560) (CBMAB-1050-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CECR2 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-2465) (CBMAB-C3533WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-F11R Recombinant Antibody (402) (CBMAB-0026-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM29 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179787) (CBMAB-A1149-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl SMC3 (K105/K106) Recombinant Antibody (V2-634053) (CBMAB-AP052LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BLNK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0623) (CBMAB-0626-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (BA0013) (CBMAB-0272CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP5F1A Recombinant Antibody (51) (CBMAB-A4043-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








