TCF4 Antibodies
Background
TCF4 is a widely expressed basic helical ring-helix (bHLH) transcription factor that mainly plays a key role in the development of the central nervous system. This protein regulates the expression of downstream genes by binding to specific DNA sequences, thereby participating in processes such as neural differentiation, cell cycle regulation, and synaptic plasticity. Research has found that abnormalities in the TCF4 gene are associated with various neurodevelopmental disorders, among which the most prominent is its pathogenic association with Pitt-Hopkins syndrome, a condition in which patients often experience intellectual disability and abnormal respiratory rhythms. Since its first identification in the 1990s, TCF4 has become an important model molecule in neurodevelopmental research. Its complex regulatory network and the functional diversity of splicing variants have continuously driven the understanding of the mechanisms of nervous system development and the pathology of diseases.
Structure of TCF4
TCF4 is a relatively large protein, and its molecular weight varies significantly due to differences in splicing isomers, ranging approximately from 65 to 90 kDa. This fluctuation mainly stems from its variable protein domain composition.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~68-85 | ~70-82 | ~69-83 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains a basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) domain for DNA binding and dimerization; And variable activation domains | The bHLH domain is highly conserved, but there are species-specific differences in the sequence and length of the activation domain | With human and mouse TCF4 high homology in the core function, the structure area is different |
The amino acid sequence length of this protein varies due to its abundant alternative splicing, but all isomers share a conserved basic helical-ring-helix (bHLH) domain, which is at the core of its function as a transcription factor. This domain enables it to form homologous or heterodimers (for example, with ASCL1) and specifically bind to the target DNA sequence (E-box). The tertiary structure of the protein is dominated by this highly ordered bHLH motif, which forms two α -helices separated by a ring-shaped region, jointly constituting the DNA binding interface. Its transcriptional activation function depends on the relatively flexible and variable C-terminal activation domain, which regulates gene expression by recruiting other coactivator complexes.
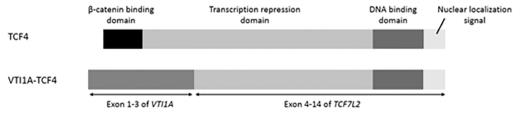 Fig. 1 Structural Domains of Wildtype TCF4.1
Fig. 1 Structural Domains of Wildtype TCF4.1
Key structural properties of TCF4:
- Alkaline helical ring-helical (bHLH) domain
- Highly variable activation domain
- Polyglutamine sequence region
Functions of TCF4
The main function of the TCF4 gene is to regulate gene expression as a transcription factor. However, it is also widely involved in a variety of key biological processes, including neural development, cell fate determination, and tumorigenesis.
| Function | Description |
| Transcriptional regulation | As a core transcription factor, it activates or inhibits the expression of downstream target genes by binding to specific DNA sequences such as E-box. |
| Neural development | In the play a key role in the development of the central nervous system, regulate the proliferation and differentiation of neural precursor cells, migration and the formation of neuronal circuits. |
| Cell cycle and differentiation | Involved in cell cycle control process and determine a variety of cell types (especially the epithelial cells and neurons) differentiation of fate. |
| Tumor suppression/promotion | Depending on the cellular environment, it can exert the dual functions of tumor suppressor genes or proto-oncogenes, and its imbalance is associated with various cancers, such as colorectal cancer. |
| Synaptic plasticity | Regulating synaptic plasticity and neuronal function related to learning and memory, its functional abnormalities are closely related to cognitive impairment. |
Unlike multi-subunit transcriptional complexes with synergistic effects, TCF4 typically functions in a dimer form (often paired with other bHLH proteins such as ASCL1), and its DNA binding curve is more similar to the specific binding of monomers, emphasizing its precise on-off role in initiating specific gene expression programs.
Applications of TCF4 and TCF4 Antibody in Literature
- Tu, Wei, et al. "TCF4 enhances hepatic metastasis of colorectal cancer by regulating tumor-associated macrophage via CCL2/CCR2 signaling." Cell death & disease 12.10 (2021): 882. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-04166-w
The article indicates that in liver metastasis of colorectal cancer, TCF4 promotes the recruitment of tumor-associated macrophages and M2 polarization by up-regulating the CCL2/CCR2 axis, thereby driving metastasis. Targeting this axis can inhibit the liver metastasis process in mouse models.
- Lee, Geun Taek, et al. "TCF4 induces enzalutamide resistance via neuroendocrine differentiation in prostate cancer." PloS one 14.9 (2019): e0213488. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0213488
The article indicates that in prostate cancer, TCF4 drives enzalutamide resistance by mediating neuroendocrine differentiation and upregulating PTHrP. Inhibiting TCF4 or PTHrP can partially reverse drug resistance, providing a new treatment strategy.
- Zhang, Tao, et al. "TCF7L2 promotes anoikis resistance and metastasis of gastric cancer by transcriptionally activating PLAUR." International Journal of Biological Sciences 18.11 (2022): 4560. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.69933
The article indicates that in gastric cancer, TCF7L2 promotes cell nest loss, apoptosis resistance and metastasis by transcriptional activation of PLAUR. The high expression of both suggests a poor prognosis and is a potential therapeutic target for anti-metastasis.
- Davidsen, Johanne, et al. "The VTI1A-TCF4 colon cancer fusion protein is a dominant negative regulator of Wnt signaling and is transcriptionally regulated by intestinal homeodomain factor CDX2." PloS one 13.7 (2018): e0200215. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0200215
The article indicates that in colorectal cancer, approximately 3% of cases have VTI1A-TCF4 gene fusions. This fusion protein was identified as a dominant negative regulator of the Wnt pathway, and its VTI1A promoter is activated by the transcription factor CDX2.
- Yu, Nanlan, et al. "MAD2B acts as a negative regulatory partner of TCF4 on proliferation in human dermal papilla cells." Scientific Reports 7.1 (2017): 11687. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10350-w
The article indicates that in hair follicle development, MAD2B interacts physically with TCF4 and inhibits its transcriptional activity, antagonizing the proliferation of dermal papillary cells and the expression of growth-promoting cytokines induced by TCF4, thereby negatively regulating the Wnt signaling pathway.
Creative Biolabs: TCF4 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality TCF4 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom TCF4 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our TCF4 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Davidsen, Johanne, et al. "The VTI1A-TCF4 colon cancer fusion protein is a dominant negative regulator of Wnt signaling and is transcriptionally regulated by intestinal homeodomain factor CDX2." PloS one 13.7 (2018): e0200215. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0200215
Anti-TCF4 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (ALB9) (CBMAB-0176CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-4-Hydroxynonenal Recombinant Antibody (V2-502280) (CBMAB-C1055-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-2C TCR Recombinant Antibody (V2-1556) (CBMAB-0951-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CA9 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2079) (CBMAB-C0131-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AFM Recombinant Antibody (V2-634159) (CBMAB-AP185LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503417) (CBMAB-V208-1369-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (BA0013) (CBMAB-0272CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD247 Recombinant Antibody (6B10.2) (CBMAB-C1583-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-FLI1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0733) (CBMAB-F0435-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CCDC6 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0106) (CBMAB-C5397-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CAP219) (CBMAB-AP536LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD2AP Recombinant Antibody (BR083) (CBMAB-BR083LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B1 Recombinant Antibody (E4) (CBMAB-0463-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCND2 Recombinant Antibody (DCS-3) (CBMAB-G1318-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARHGAP5 Recombinant Antibody (54/P190-B) (CBMAB-P0070-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-A2M Recombinant Antibody (V2-178822) (CBMAB-A0036-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0790) (CBMAB-0793-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl-α-Tubulin (Lys40) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623485) (CBMAB-CP2897-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7719) (CBMAB-1898CQ)

-
Rat Anti-CD300A Recombinant Antibody (172224) (CBMAB-C0423-LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








