WEE1 Antibodies
Background
WEE1 gene encodes a key nuclear protein kinase and mainly functions as a core regulator of cell cycle checkpoints. This protein inhibits the activity of CDK1/2 through phosphorylation, preventing cells from transitioning from the G2 phase to the M phase before DNA damage is repaired, thereby maintaining genomic stability. In tumor cells, the regulatory mechanism of WEE1 is often disrupted, making it an important target for cancer treatment. This gene was first identified in 1993. Its name is derived from the Scottish word for "small", implying that yeast strains lacking this gene would produce smaller cells due to premature entry into mitosis. As a classic model in the field of cell cycle research, the discovery of the WEE1 gene has greatly advanced our understanding of DNA damage response, cell cycle checkpoints and tumorigenesis mechanisms. Currently, the related inhibitors have entered the clinical trial stage for various malignant tumors.
Structure of WEE1
WEE1 protein is a serine/threonine kinase with a molecular weight of approximately 94 kDa. There are certain differences in its molecular weight among different species, which is mainly due to the evolutionary variation of the gene coding sequence.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebrafish | African clawed toad | Fruit fly |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 94 | 95.2 | 96.5 | 93.8 | 105.6 |
| Primary Structural Differences | N-terminal kinase domain structure and the C control area | Homology with human is up to 90% | Retain the core kinase domain | Highly expressed during embryonic development | The structure is relatively simplified |
This protein is composed of 651 amino acids, and its spatial structure shows a typical protein kinase folding. The core functional region of WEE1 contains a highly conserved ATP-binding pocket and substrate recognition region, exerting kinase activity through the N-terminal domain. The active center of this protein achieves substrate-specific recognition through the arginine-serine-lysine conserved motif. The asparagine residue in its catalytic ring is crucial for the phosphate transfer reaction, while the conformational change of the activation ring directly regulates the enzyme's active state.
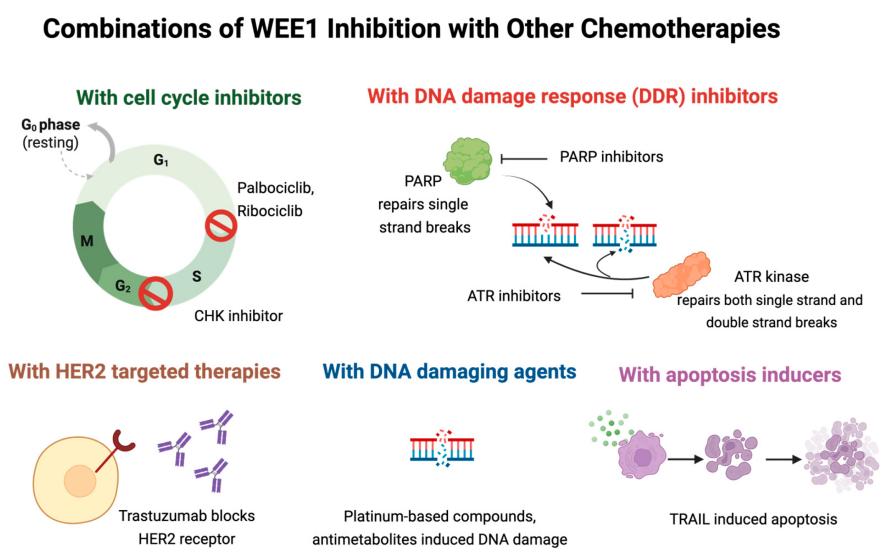 Fig. 1 WEE1 inhibitors combined with other agents in preclinical models.1
Fig. 1 WEE1 inhibitors combined with other agents in preclinical models.1
Key structural properties of WEE1:
- Typical bilobed domains of protein kinases
- Conservative ATP-combined pocket and substrate recognition interface
- Key kinase activity centers and regulatory modules
Functions of WEE1
The core function of the WEE1 gene is to serve as a key regulatory factor for the G2/M checkpoint in the cell cycle. However, it is also involved in a variety of cellular processes, including DNA damage repair, maintenance of genomic stability and regulation of cell differentiation.
| Function | Description |
| Cell cycle arrest | By phosphorylating the Tyr15 site of CDK1 to inhibit its activity, it prevents cells from entering mitosis before DNA damage is repaired. |
| Maintenance of genomic stability | As an important effector of the DNA damage response pathway, it prevents damaged DNA from being replicated and transferred to progeny cells. |
| Tumor suppression mechanism | In a wide variety of cancer in its function disorder lead to genomic instability, make it a potential target of cancer therapy. |
| Chemotherapy-sensitizing effect | WEE1 inhibitors can relieve G2/M block, forcing DNA-damaged cells to enter division and triggering apoptosis. |
| Regulation of embryonic development | By precisely regulating the cell cycle process, it influences the cell proliferation pattern during the early embryonic development. |
The activity regulation of WEE1 shows a strict cell cycle dependence. Its protein level peaks in the S/G2 phase and rapidly degrades after the M phase. This dynamic expression pattern is highly consistent with its functional positioning as a "brake" of the cell cycle.
Applications of WEE1 and WEE1 Antibody in Literature
1. Ghelli Luserna di Rorà, Andrea, et al. "A WEE1 family business: regulation of mitosis, cancer progression, and therapeutic target." Journal of hematology & oncology 13.1 (2020): 126. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-00959-2
This article focuses on the WEE1/PKMYT1 kinase and reviews its dual roles in the cell cycle and DNA damage repair: tumor suppression in normal cells and pseudooncogenization in cancer cells. The article summarizes the relevant molecular alterations and preclinical studies, and explores the efficacy data of WEE1/PKMYT1 inhibitors used alone or in combination with radiotherapy, chemotherapy and other targeted drugs.
2. Kong, Anthony, and Hisham Mehanna. "WEE1 inhibitor: clinical development." Current oncology reports 23.9 (2021): 107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-021-01098-8
The article indicates that WEE1 inhibitors can enhance the sensitivity to radiotherapy and chemotherapy, but their clinical development is limited by the relatively high toxic reactions when used in combination. TP53 mutation is not the most reliable biomarker for predicting its efficacy. Current research is exploring its combination regimens with new drugs such as ATR/PARP inhibitors or immunotherapies, with the aim of achieving breakthroughs in efficacy and safety.
3. Nonneville, Alexandre, et al. "WEE1 dependency and pejorative prognostic value in triple‐negative breast cancer." Advanced Science 8.17 (2021): 2101030. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202101030
The article indicates that WEE1 kinase plays a key role in inhibiting triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Studies have confirmed that TNBC has a higher dependence on WEE1, and its high expression predicts a poor prognosis. The combination of WEE1 inhibitors and BCL-XL inhibitors provides a new targeted therapeutic strategy for TNBC that is insensitive to CDK4/6 inhibitors due to RB deficiency and other factors.
4. Fukuda, Koji, et al. "Targeting WEE1 enhances the antitumor effect of KRAS-mutated non-small cell lung cancer harboring TP53 mutations." Cell Reports Medicine 5.6 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101578
The treatment for KRAS-mutated lung cancer is limited due to the drug resistance mechanism. Research has found that WEE1 inhibitors can effectively enhance the apoptosis of TP53 co-mutated cancer cells, and the mechanism is related to disrupting DNA damage repair and inducing mitotic disasters. The combined use of KRAS-G12C and WEE1 inhibitors can synergistically inhibit tumor growth.
5. Zhang, Zhao, et al. "Targeting WEE1 Kinase for Breast Cancer Therapeutics: An Update." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26.12 (2025): 5701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125701
The article indicates that WEE1 kinase is a key protein regulating cell mitosis and has become a therapeutic target in various cancers. Although the clinical efficacy of its inhibitor Adavosertib varies among individuals, several new WEE1 inhibitors are under development. Preclinical studies have shown that they may be able to induce immune-related antigens, providing new strategies for the treatment of breast cancer.
Creative Biolabs: WEE1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality WEE1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom WEE1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our WEE1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Zhang, Zhao, et al. "Targeting WEE1 Kinase for Breast Cancer Therapeutics: An Update." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26.12 (2025): 5701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125701
Anti-WEE1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7719) (CBMAB-1898CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-EGR1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-100) (CBMAB-Z0289-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-AZGP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-007) (CBMAB-Z0012-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-CHRNA9 Recombinant Antibody (8E4) (CBMAB-C9161-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-A2M Recombinant Antibody (V2-178822) (CBMAB-A0036-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ABL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179121) (CBMAB-A0364-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0442) (CBMAB-0445-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD2AP Recombinant Antibody (BR083) (CBMAB-BR083LY)

-
Mouse Anti-COL12A1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C3117) (CBMAB-C4560-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ABIN2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179106) (CBMAB-A0349-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-EMP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0100) (CBMAB-E0207-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CAPZB Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0944) (CBMAB-C2381-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD247 Recombinant Antibody (6B10.2) (CBMAB-C1583-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1A2 Recombinant Antibody (M7-PB-E9) (CBMAB-A4013-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL2L1 Recombinant Antibody (H5) (CBMAB-1025CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AOC3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0014) (CBMAB-0014-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (H14) (CBMAB-E1341-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCDC6 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0106) (CBMAB-C5397-CQ)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR-0120) (CBMAB-R0120-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-APC Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A661) (CBMAB-A3036-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






