ALDOA Antibodies
Background
ALDOA is a key glycolytic enzyme, mainly found in the skeletal muscle and embryonic tissues of vertebrates. This protein catalyzes the reversible cleavage of fructose 1, 6-diphosphate into dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. It also possesses non-enzymatic actin binding capabilities and regulates cellular energy metabolism and structural integrity. ALDOA is often overexpressed in tumor cells and maintains the rapid proliferation requirements of cancer cells by promoting aerobic glycolysis (Wabberg effect). Its tetramer structure was analyzed by X-ray crystallography in the 1970s. The typical (β/α) 8-barrel folding pattern provides a classic model for studying enzyme catalytic mechanisms and has significant scientific value for understanding metabolic regulation, cytoskeletal recombination, and tumor metabolic reprogramming.
Structure of ALDOA
ALDOA is a protein with a molecular weight of approximately 39 kDa, and its precise molecular weight varies slightly among different species.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Bovine | Zebrafish | Chicken |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 39.4 | 39.5 | 39.2 | 39.8 | 39.3 |
| Primary Structural Differences | The typical (β/α)8 Barrel fold, was composed of 363 amino acids. | With human ALDOA 90% sequence homology | Conserved active site aspartic acid | There are two specific lysine residues | The C-end domain is highly conservative |
This protein is composed of approximately 220 amino acids, forming a characteristic adenylate kinase folding structure. This protein is composed of eight parallel β chains encircled by eight α -helices, forming a classic TIM barrel structure. The active center is located in the crack formed at the C-end of the β chain. The conserved substrate binding sites contain key catalytic residues: lysine 107 is responsible for forming the Schiff base intermediate, aspartic acid 33 acts as an acid-base catalyst, and glutamic acid 34 is responsible for the stability of the enediol salt during the substrate cleavage process. Four identical subunits assemble into an active tetramer through salt Bridges and hydrophobic interactions at the interface. This quaternary structure is crucial for its catalytic activity and allosteric regulation.
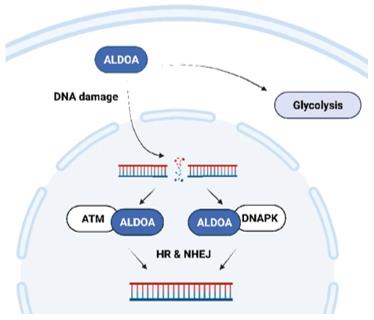 Fig. 1 The schematic shows a proposed mechanism of ALDOA-dependent regulation of DNA DSB repair.1
Fig. 1 The schematic shows a proposed mechanism of ALDOA-dependent regulation of DNA DSB repair.1
Key structural properties of ALDOA:
- Typical (β/α)8 barrel fold conformation
- The active center is located in the catalytic cleft formed at the C-terminus of the β chain
- Conservative catalytic triad (Lys107, Asp33, Glu34)
- Four dimer interface stability through salt bridge network structure
Functions of ALDOA
The core function of ALDOA is to catalyze reversible reactions in glycolysis. In addition, it is also involved in a variety of cellular processes, including the organization of the cytoskeleton and the regulation of gene transcription.
| Function | Description |
| Glycolytic catalysis | Catalyzing the cleavage of fructose 1, 6-diphosphate to dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is a key step in the glycolytic pathway. |
| Regulation of metabolic flux | The flow direction of carbon sources in glycolysis is regulated by the reaction rate to influence the energy supply of cells. |
| Cytoskeleton binding | Combined with actin microfilament, coordination of energy metabolism and maintain cells form and movement process. |
| Transcriptional regulation | Within the nucleus as a transcriptional regulation factor, influence the expression of certain genes. |
| Tumor metabolic reprogramming | In the high expression of cancer cells to promote aerobic glycolysis (warburg effect), to support its rapid proliferation. |
The kinetic characteristics of this enzyme are manifested as a typical Mie equation curve, which is different from the S-shaped deformation structure regulation curve of rate-limiting enzymes. This reflects its role as a core catalytic enzyme in metabolic pathways, responsible for maintaining the stable operation of basic energy metabolism.
Applications of ALDOA and ALDOA Antibody in Literature
1. Wang, Xinyue, et al. "A novel rabbit anti-myoglobin monoclonal antibody’s potential application in rhabdomyolysis associated acute kidney injury." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.9 (2023): 7822. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-021-02148-y
This study confirmed that POU2F1 is highly expressed in colon cancer and is associated with a poor prognosis. By directly binding to the ALDOA promoter, it enhances glycolysis and pentose phosphate pathways, promotes tumor proliferation and oxaliplatin resistance. The POU2F1-ALDOA axis is a potential therapeutic target.
2. Han, Lijie, et al. "LIPH contributes to glycolytic phenotype in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by activating LPA/LPAR axis and maintaining ALDOA stability." Journal of Translational Medicine 21.1 (2023): 838. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-023-04702-6
Studies have revealed that LIPH significantly promotes tumor glycolysis and proliferation in pancreatic cancer by activating the LPA/LPAR signaling axis and maintaining ALDOA stability. For tumors with high expression of LIPH, the new therapy of gemcitabine combined with targeted drugs has shown good efficacy.
3. Chen, Haidi, et al. "ALDOA inhibits cell cycle arrest induced by DNA damage via the ATM-PLK1 pathway in pancreatic cancer cells." Cancer Cell International 21.1 (2021): 514. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-021-02210-5
Research reveals that ALDOA promotes the development of pancreatic cancer by inhibiting the ATM signaling pathway, hindering DNA damage repair and reversing cell cycle arrest. The mechanism is related to the activation of PLK1 and the weakening of cellular self-surveillance.
4. Sobanski, Thais, et al. "The fructose-bisphosphate, Aldolase A (ALDOA), facilitates DNA-PKcs and ATM kinase activity to regulate DNA double-strand break repair." Scientific Reports 13.1 (2023): 15171. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-41133-1
This study reveals the direct role of ALDOA in the repair of DNA double-strand breaks. After DNA damage, ALDOA enters the nucleus and interacts with DNA-PK/ATM, promoting its phosphorylation and thus effectively completing damage repair. This discovery provides a new strategy for simultaneously targeting tumor metabolism and DNA repair.
5. Song, Junjiao, et al. "Aldolase A accelerates cancer progression by modulating mRNA translation and protein biosynthesis via noncanonical mechanisms." Advanced Science 10.26 (2023): 2302425. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202302425
Research reveals that ALDOA interacts with IGF2BP1 through non-catalytic function, stabilizes eIF4G mRNA to accelerate protein synthesis, thereby promoting the progression of liver cancer. siRNA targeting ALDOA can effectively inhibit tumors, demonstrating its therapeutic potential.
Creative Biolabs: ALDOA Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality ALDOA antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom ALDOA Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our ALDOA antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Sobanski, Thais, et al. "The fructose-bisphosphate, Aldolase A (ALDOA), facilitates DNA-PKcs and ATM kinase activity to regulate DNA double-strand break repair." Scientific Reports 13.1 (2023): 15171. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-41133-1
Anti-ALDOA antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rabbit Anti-CCN1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-3580) (CBMAB-C4816WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD2AP Recombinant Antibody (BR083) (CBMAB-BR083LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ASB9 Recombinant Antibody (1D8) (CBMAB-A0529-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CGAS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-0995) (CBMAB-M1146-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM12 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179752) (CBMAB-A1114-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B1 Recombinant Antibody (E4) (CBMAB-0463-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AGK Recombinant Antibody (V2-258056) (CBMAB-M0989-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALDOA Recombinant Antibody (A2) (CBMAB-A2316-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-180650) (CBMAB-A2186-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-GFP Recombinant Antibody (28) (CBMAB-G3038-LY)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR-0120) (CBMAB-R0120-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CTCF Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2371) (CBMAB-C2443-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BRD3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0801) (CBMAB-0804-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTG1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179597) (CBMAB-A0916-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-APOE Recombinant Antibody (A1) (CBMAB-0078CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (D9S6V) (CBMAB-CP0017-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXA3 Recombinant Antibody (2A9) (CBMAB-0377-YC)

-
Rat Anti-CD63 Recombinant Antibody (7G4.2E8) (CBMAB-C8725-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503416) (CBMAB-V208-1402-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-APOH Recombinant Antibody (4D9A4) (CBMAB-A3249-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






